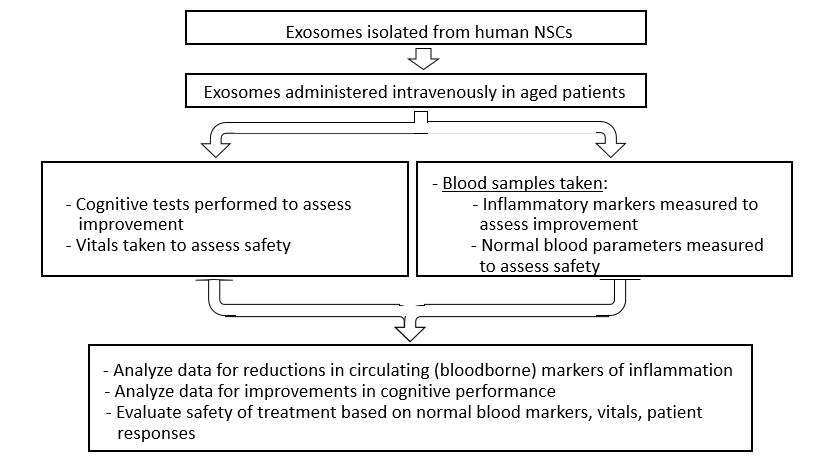
Current Study: Neural stem cell exosomes for human aging-associated neuroinflammation and cognitive decline
Exosome-based Therapy for Hypothalamic Inflammation (HI) and Other Brain Pathologies
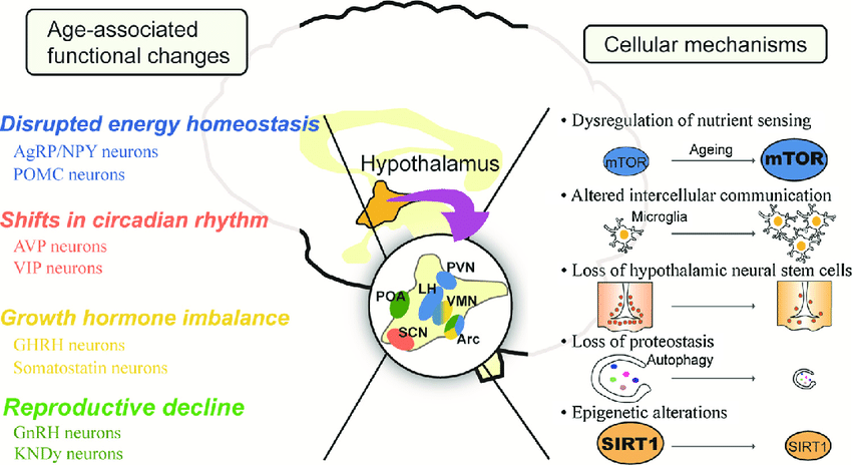
- Hypothalamic inflammation (HI) is associated with aging, metabolic disease and obesity through a variety of neuroendocrine pathways
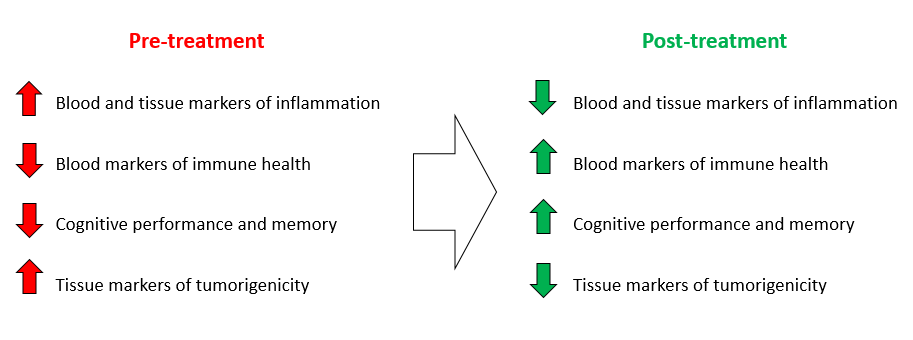
- Neural stem cells (NSCs) exert a protective and inflammation-suppressant role on the brain in aged mice
a. Found to be mediated by stem cell-derived exosomes and their therapeutic contents
b. Protective effect of NSCs has been restored experimentally through exogenous exosome application - There is evidence that NSCs and their exosomes can also promote healing of damaged neurovascular tissue in traumatic brain injury and stroke
a. NSC exosomes contain a number of factors that promote growth and tissue-healing - NSC-derived exosomes are being tested for patient applications to ameliorate aging-associated cognitive decline and dementia, as well as a variety of metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases in the brain
Experimental Design
Summary Hypothesis of Effects
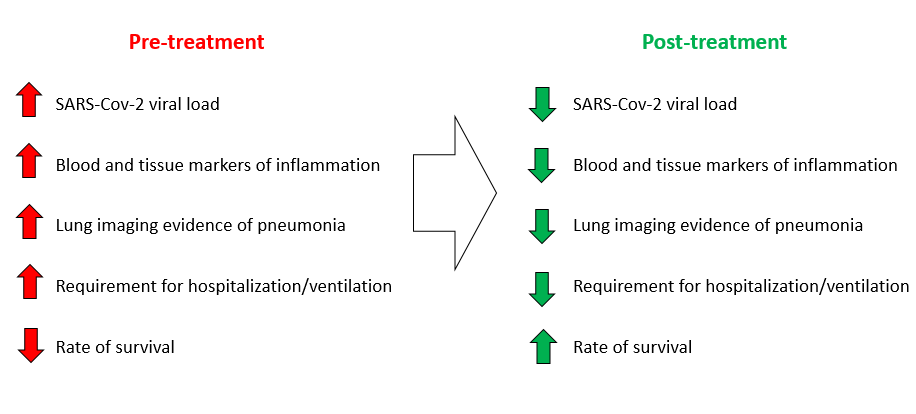
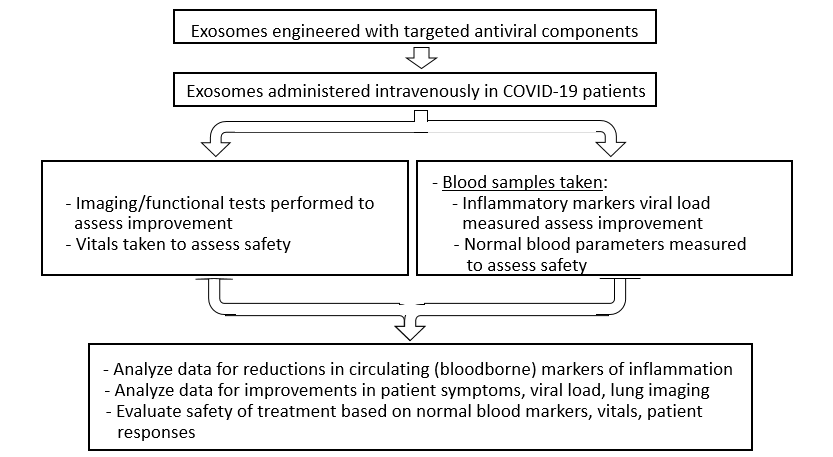
Current Study: Exosomal delivery of antiviral and cute respiratory distress therapies for COVID-19
Exosome-based Therapy for COVID-19
- COVID-19 progression is associated with a ‘cytokine storm,’ a significant elevation in inflammatory cytokines that are involved in acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), as well as causing in some cases long-term damage to multiple organ systems.
- Exosomes can be used to deliver contents that suppress the cytokine storm, thereby reducing respiratory distress and organ damage.
- We are also engineering specific viral-targeted constructs that can be delivered by exosomes to cells in order to ‘deactivate’ the SARS-Cov-2 virus that causes COVID-19.
Experimental Design
Summary Hypothesis of Effects